Overhead Cost: Type, Examples & Its Impact on Business
Kelvin ramps up its production to 15,000 thermometers per month, and its variable overhead correspondingly rises to $30,000, resulting in the variable overhead remaining at $2.00 per unit. Advertising costs aren’t directly related to producing goods and services for a business, but they are important for promoting growth and increasing profits. Whether advertising is a large overhead component depends on your business budget, strategy, and promotional goals. Overhead costs, also called operating expenses, are all the ongoing business expenses required to run your business that are not directly involved with creating your product or service. This includes everything from office supplies to administration but excludes the cost of goods sold.
A company that has production runs of 10,000 units and a cost per unit of $1, might see a decline in the direct cost to 75 cents if the manufacturing rate is increased to 30,000 units. If the manufacturer maintains selling prices at the existing level, the cost reduction of 25 cents per unit represents $2,500 in savings on each production run. Balancing cost-cutting with growth initiatives, understanding that too much emphasis on reducing variable overheads can stifle innovation and expansion efforts. Variable overhead is a dynamic component of business finances that requires careful monitoring and management. By understanding and controlling these costs, businesses can maintain financial flexibility and improve their overall financial health.
Overhead costs and direct costs are two essential components of a business’s financial structure, but they serve different purposes and are categorized differently. Understanding the distinction between these costs is critical for effective budgeting, pricing, and financial analysis. It is the sum of those costs of general management, secretarial, accounting and administrative services, which cannot be directly related to the production.
How does variable production overhead impact product pricing?
Common fixed costs include salaries for supervisors, managers, and administrative staff, rent for buildings, and tax liabilities. The variable overhead costs for this business could include costs like electricity for running machinery, hourly wages for temporary workers, and costs of supplies like sandpaper and screws. Both fixed costs and variable costs contribute to providing a clear picture of the overall cost structure of the business. Understanding the difference between fixed costs and variable costs is important for making rational decisions about the business expenses which have a direct impact on profitability. Variable costs change directly with the output – when output is zero, the variable cost will be zero.
Overheads that cannot be classified into any of the above categories will come under this head. For instance, for a multinational company, general and administrative overheads will apply. This will include costs related to general management, such as the cost incurred for human resources, receptionists, accountants, etc. Sales overheads will include expenses incurred for marketing and sales of a product. Some other examples are research overhead, maintenance overhead, manufacturing overhead, transportation overhead, etc. Now that we have defined overheads let’s understand how an overhead cost is accounted for.
These Sources include White Papers, Government Information & Data, Original Reporting and Interviews from Industry Experts. Learn more about the standards we follow in producing Accurate, Unbiased and Researched Content in our editorial policy. Consider bundling your policies or raising your deductibles to lower your premiums.
- Additional factors that may be included in variable overhead expenses are materials and equipment maintenance.
- Semi-variable overhead can be defined as a combination of fixed and variable overheads where the overhead cost remains static up to a period of production but then increases with volume.
- Variable overhead costs represent a significant portion of the total expenses incurred by businesses across various industries.
- It not only streamlines existing processes but also opens up new avenues for cost savings and efficiency improvements.
The Difference Between Variable and Fixed Overhead Costs
- Whether you’re a finance learner or a seasoned professional, mastering variable overhead costs will enhance your ability to make informed decisions and drive business success.
- It also plays a pivotal role in decision-making processes such as make-or-buy decisions, pricing strategies, and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
- Although these are rare, they can be costly and make up a large part of that quarter’s overhead.
- Big data is a term that refers to the massive volume, variety, and velocity of data that is…
- Reducing overhead costs is essential for improving profitability and maintaining efficient business operations.
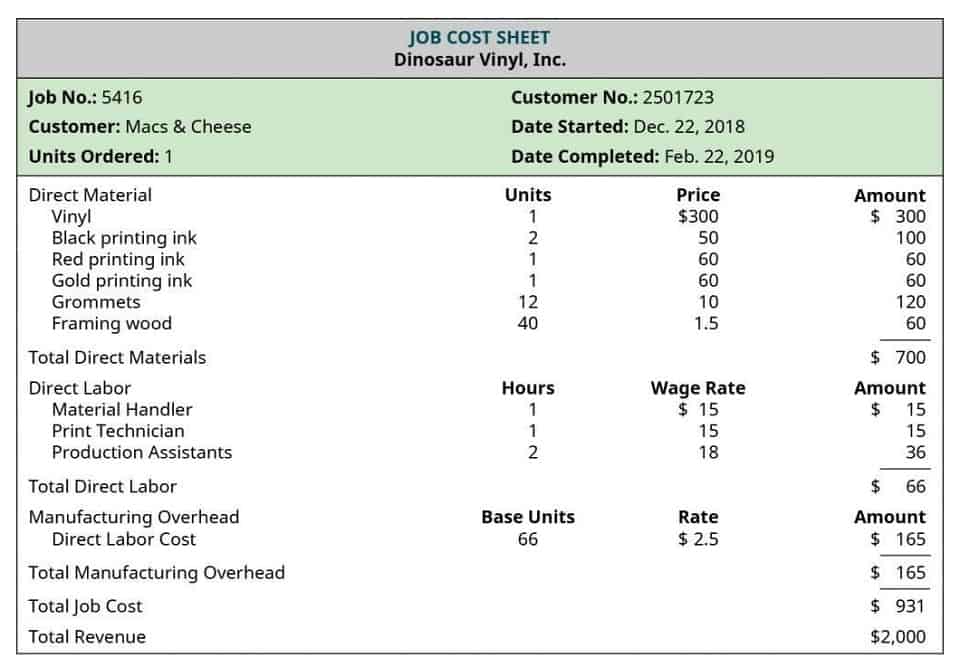
However, companies can sometimes tie fixed costs to the units produced in a particular facility. Companies can forecast variable production overhead costs using historical data, industry benchmarks, and estimates of future production levels. Production overhead refers to the indirect costs incurred during the manufacturing process, excluding direct labor and direct materials. It includes expenses such as factory rent, utilities, depreciation of production equipment, and supervisory salaries.
Variable costs are in contrast to fixed costs, which remain relatively constant regardless of the company’s level of production or business activity. Fixed production overhead costs remain constant regardless of production output, while variable production overhead costs fluctuate with the level of production. In the realm of business operations, understanding and managing costs is crucial for financial success.
The variable overhead spending concept is most applicable in situations where the production process is tightly controlled, as is the case when large numbers of identical units are produced. The variable overhead efficiency variance is the difference between the actual and budgeted hours worked, which are then applied to the standard variable overhead rate per hour. It is entirely possible that an improperly-set standard number of labor hours can result in a variance that does not represent the actual performance of an entity. By integrating these insights into their financial strategies, companies can better navigate the complexities of production costs and remain competitive in their respective markets.
Administrative Expenses
They might use regression analysis to understand how variable overhead correlates with production levels. By following these steps, businesses can ensure that their variable overhead costs are accurately reflected in their product pricing, which is essential for maintaining profitability. It’s important to remember that the calculation of variable overhead is not just a financial exercise but a tool for operational analysis and strategic planning. Through this process, companies can identify areas of inefficiency and opportunities for cost savings, ultimately leading to a stronger financial position. For a financial analyst, these could translate into variable elements within cost accounting models that impact the calculation of product cost and, ultimately, pricing strategies. An entrepreneur might view variable overheads as a lever to adjust operations swiftly in response to market demands.
This would be utilities, supplies, or rent that are necessary for production but not a direct part of the production process. For example, if demand for a manufacturing company’s product was to increase, and production was raised to compensate then the company’s energy expense would correspondingly increase. To overcome these challenges, I recommend using activity-based costing (ABC) for more accurate allocation and regularly reviewing supplier contracts to lock in favorable rates.
Budgeting and Forecasting
From the perspective of a cost accountant, variable overhead is crucial for preparing accurate product costings and budgets. It includes costs such as utilities, raw materials, and labor hours, which are not fixed and can vary month-to-month. For a financial analyst, understanding variable overhead is key to analyzing a examples of variable overhead costs company’s operational efficiency and profitability. High variable overhead costs might indicate inefficiencies or potential areas for cost savings. Variable overhead costs are a type of indirect manufacturing cost that fluctuates in proportion to changes in the level of production or business activity.
A clear understanding of overhead expenses is essential for accurate budgeting and financial planning. Monitoring these costs allows businesses to anticipate future expenses, allocate resources effectively, and avoid cash flow issues. Monitoring overhead costs is a vital component of effective financial management and long-term business success. While these expenses may not directly generate revenue, their impact on profitability, operational efficiency, and decision-making cannot be underestimated.
Calculating overhead costs accurately is essential for managing budgets, pricing products or services, and improving business profitability. The process involves identifying all indirect expenses, classifying them, and using the data to compute the overhead rate. Variable costs increase or decrease depending on a company’s production volume; they rise as production increases and fall as production decreases. Examples of variable costs include the costs of raw materials and packaging. Cost accounting is a form of managerial accounting that aims to capture a company’s total cost of production by assessing its variable and fixed costs. A direct cost is a price that can be directly tied to the production of specific goods or services.